Our Approach
Our body’s immune cells detect damaged and non-self cells through complex interactions, scanning their milieu for glycosylation patterns presented on the surface of all cells. At Aviceda, we pioneered technology to improve on nature’s design with our vast library of high affinity synthetic ligands to modulate the body’s immune response.
Aviceda’s platform technology HALOS™ (High-Affinity Ligands of Siglecs) takes immune checkpoint inhibitors to the next level with Sialic Acid Mimetics (SAMs). SAMs can access the superfamily of checkpoint inhibitors through the same tested PD-1/PD-L1 intracellular pathways of ITIM (Immunoreceptor Tyrosine-based Inhibitory Motif) domains, but extend immune cell engagement beyond only T-cells, allowing us to modify the behavior of most classes of innate and adaptive immune cells.
Identifying the immune modulators
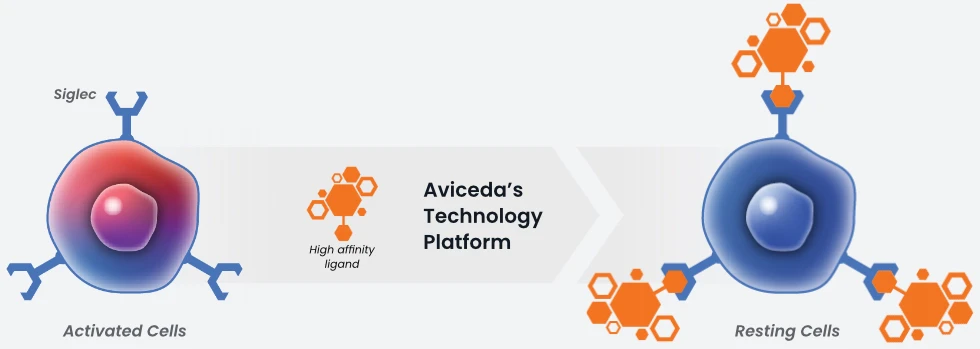
Siglecs (Sialic-Acid binding Immunoglobulin Like Lectins) are receptors present on the surface of all immune cells. They are responsible for regulating the immune response of those cells (on/off) depending on their interactions with glyco-binding ligands.
Lock and key specificity
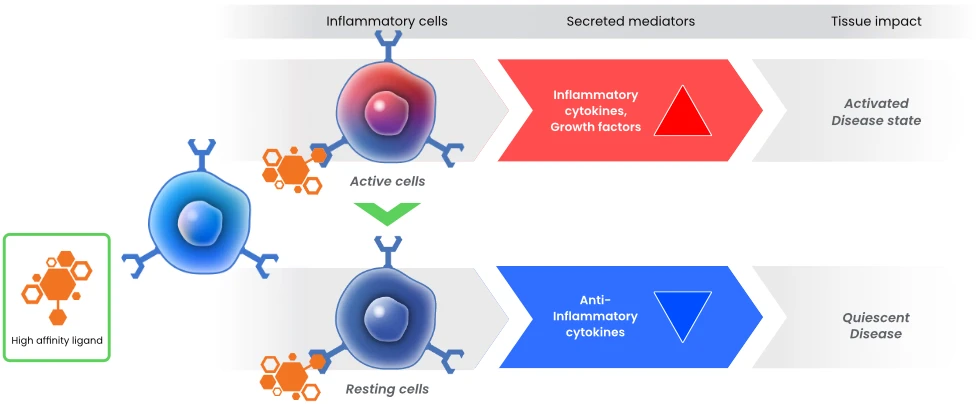
In nature, Siglecs engage extracellular sialic acid based motifs in a highly selective manner. This interaction activates an intracellular biochemical cascade which activates ITIM in a manner like that seen in the PD-1/PDL1 checkpoint pathway. Aviceda’s proprietary HALOS™ technology synthesizes ligands which have greater binding affinity to Siglecs than nature’s cell-derived ligands, antibodies, or other small molecules. Aviceda’s molecules are “Immune Cell Engagers,” with the ability to specifically target different immune cells with precision.
Designing the key
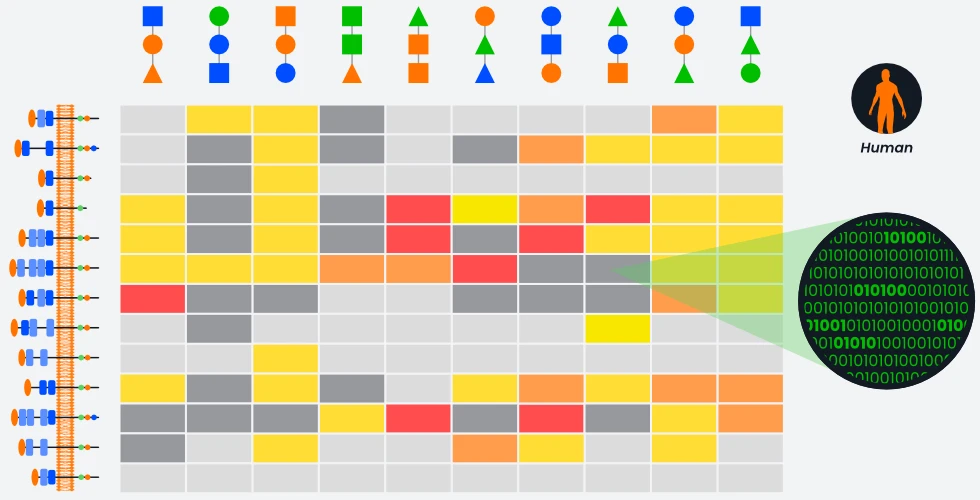
Through Aviceda’s proprietary high throughput screening library of manufactured ligands, we can develop synthetic ligands that have the highest specificity and affinity to Siglecs, orders of magnitude higher than naturally occurring ligands. Furthermore, our proprietary technology allows us to naturally and powerfully create multivalent ligands, increasing our ability to modulate a variety of immune cells.
